Absolute beginner's guide to scripting
Introduction
This tutorial shows how to do some basic scripting. It explains how to script in the simplest terms possible, and is designed for people with little or no experience with scripting. And also reading speical books on scripting will help you understand more.
What is scripting?
Scripting is a way to tell the game what to do. However, computers can only understand commands if you tell them exactly what to do, in a specific code. ROBLOX Scripts are commands in a coding language called Lua. Lua is not-so-hard to understand, depending on the way you want to use it.
Your first script
Already you're about to make your very first script. We'll be executing the script from a place in ROBLOX Studio called the Command Bar, which allows you to execute a single line of script instantly.
Being specific
Let's make the most basic script: a suicide script. When it executes, it kills you. Scripting is just giving commands to the computer.
How do you kill a player? There are two ways to kill a character: disconnect their Head from their Torso, or have their Humanoid's health dropped to zero. Don't worry what a Humanoid is, we'll use the first method for right now.
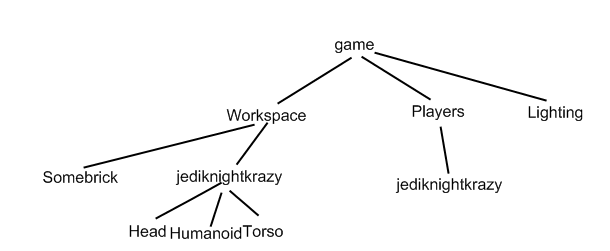
The game doesn't know whom to kill, until you specify the username of the person whom you want to kill. Think of the structure of a ROBLOX game as a tree. The trunk is called "game". Then there is a branch, called "Workspace". Think of all the bricks as branches on that "Workspace" branch. (Bricks, by the way, are not stored by their position in the game. They are organized like leaves on the branches of this tree.) You are going to be a branch, called by your username, on the "Workspace" branch, on the "game" trunk.
Note that both the Players and the Workspace branch has a branch named after a specific user "jediknightkrazy". That's because there are two branches named after you, your player, and your character.
Translating to Lua
A script needs to be in a special coding language called Lua. This section will walk you through translating a basic English command to Lua.
Here's our starting command:
Delete jediknightkrazy's head
Naturally, ROBLOX won't like that very much. Remember the tree from the last section? First we have to tell ROBLOX where to find "jediknightkrazy"
In the game, in the Workspace, there is jediknightkrazy's Head
In Lua, you go down the tree like this by using a dot: (.)
delete game.Workspace.jediknightkrazy.Head
This is almost a working statement. Now, to actually delete the head, a function must be used. To use a function, just type a colon (:) after the object you want to execute it on (in this case, Head), and then the function you want to use, which in this case, is "Remove". Then, put a pair of parentheses after the function name.
game.Workspace.jediknightkrazy.Head:Remove()
If your name isn't jediknightkrazy, substitute your name for mine:
game.Workspace.SomeGuy.Head:Remove()
To experiment a bit, try deleting the Torso instead.
Testing the script
Open ROBLOX Studio and click File > New. Add a baseplate and a spawn.
To add a baseplate: Click Insert in the game window, NOT in the menu. Select "Free Models" in the drop down list at the right of the screen. Type "baseplate" and click Search. Add one that looks good.
To add a spawn: Select "Game Objects" in the drop-down list and click on a grey (neutral) spawn. + Now, in the menu, click Tools > Test > Visit Solo. This is where you can test your places without uploading them! + Once it loads, right click in the Toolbar and check Command if it isn't checked already. A small textbox bar labelled "Command" should appear at bottom of the screen. In there, type: +
game.Workspace.Player.Head:Remove()
Don't replace Player with your username in Test mode, because your name is always "Player" in Test mode. Type it, don't just copy and paste! Hit enter. If your head vanishes and you die, you've done it! You've made your first script. Now, try your Torso. Maybe remove the Baseplate; it's probably called "Base". (HINT: It's not in Player)
Setting values and making objects
What about actually changing the value of an object, as opposed to removing an object? Earlier it was mentioned that there were two ways to kill someone. The more complicated way is setting one's Health to 0. The Health is contained in a Humanoid object, which is contained within the character (Player.Humanoid.Health).
Example:
game.Workspace.Player.Humanoid.Health
However, what about setting a value? In Lua, you set a value with the = sign. Put what you want to set on the left, and what you want to set it to on the right:
game.Workspace.Player.Humanoid.Health = 0
Type it in the command bar like before, and you should be able to kill yourself without beheading yourself.
Getting a script in your place
To make a script in ROBLOX Studio, just click Insert>Object...>Script, then you've got a script you can edit in your own place. To learn how to make useful scripts, I recommend trying to read an existing script, like a Reset Tool or a deadly block. Try modifying it to do different things.
Adding a script
Remember to use ROBLOX Studio, NOT "build", or "solo" to edit your scripts. Just click on Insert > Object, then double-click on Script. [TODO: Add picture] This script will execute as soon as your place loads, so none of the killing scripts from last tutorial are going to work in your place.
IMPORTANT: When a script encounters an error, it stops running, or breaks. So, if only half of your script gets run, there's a good chance that there's a problem somewhere in the middle.
Editing a script in ROBLOX Studio
To edit a script, find it in the Explorer window:
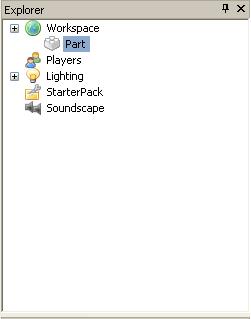
and double-click on it. Now it should open up a text editor that says
print("Hello World")
"What does 'print()' do?", you ask. Print() simply prints that line into the Output Window. To show it, click View > Output. Click the Play button in toolbar and look in the Output Window.
Testing your script
To test open the Test mode as described before. This time, don't type anything in the Command bar. They should run automatically.
Script Creation
There are 5 topics that will be answered here:
- Creating the Script
- Tagging Objects
- The Listening Event
- The Function
- Modifying Objects/Tags
NOTE: All work, building and scripting, should be done in Edit Mode. All these lessons will be shown as if you are in Edit Mode. To open Edit Mode, on your desktop screen, hit Start>Programs>ROBLOX>ROBLOX Studio. Then go to your profile, then click "Edit".
Creating the Script
What work to be done when you don't have the project? To get a script go in Roblox Studio or Solo Mode then simply select Insert>Object. Now a window will show up. In the box click on the script object. You should find the script inside"Workspace" in the explorer tab. If you don't see any explorer window up, go to View>Explorer.
Now to open the script, just double-click it. If you did it right, a window will cover the whole ingame screen, and the browser should look a bit more like Microsoft Word. And you will find the line "print("Hello World!")" Before you start, just go ahead and delete that line.
Tagging Objects
You got a nice script up, but what good is a script if it doesn't have anything to play with? Assuming the script is still under Workspace, that is where your script will run under. Let's say you want a brick turning invisible/visible, back and forth when touched. The script needs to know where that brick is before modifying it.
Now, tagging objects are not necessary, but it can make scripting a lot less work. Here's an example of tagging objects:
brick = game.Workspace.Brick
That will tag the brick under the name you assigned. You can set the name to absolutely anything. You can have as many tags as you want.
If you didn't tag it, every time you try making the script modify the object (explained in lesson 5), you would have to put the line "game.Workspace.Brick" every single time. Tags are much simpler, since you'd only have to put the name you assigned. Name the brick desired to "Brick", and tag it in the script by typing the example above. Note that tagging is the same as assigning a variable.
The Listening Event
Now we're getting into the meat of scripting. Sure, the script knows where the brick is, but that's all. It can't do anything else. Now we're jumping into a listening event.
What is a listening event? It's the trigger of the script. This is going to tell the script to do something if the listener finds the trigger fired. This is one important part of the script, otherwise you couldn't really make scripts wait for anything.
You still should have the script with the tag in it. We're going to make the script listen for being touched. Here's an example:
brick.Touched:connect(onTouch)
If the brick is Touched, It will connect the (function). The function is explained next lesson. Keep in mind that the name inside the parentheses is the name of the function. You can name this anything, however, I recommend doing the above for this lesson before you jump into any other names.
This is not the only listener type. There are many more to use, some of which require some familiarity with scripting. Here is a very well-done reference page set up by MrDoomBringer.
This is where you can find more help in the future, when you begin to understand scripting more. Not only does it show Events, but also shows other scripting references need for other aspects of scripting (some of which is explained in lesson 5).
So for this lesson, put the line "brick.Touched:connect(onTouch)" a line or two below the tag from last lesson.
The Function
Your script is getting better and better, but where is the function? Your script will break if it doesn't have one of those for the listener to refer the script to.
What is a function? It is where all your modifying work will be done. It is also an important part to your scripting. Without it, you could not make the script modify objects from listeners. Another example:
function onTouch(part) end
There is the function. As you can see, the function has "onTouch". The listener from last lesson is trying to refer to the function. The listener is going to tell the script to run through this function and do whatever is found inside (this will be explained next lesson). Notice after "onTouch". This is the tag of the object that the listener found that touched the brick. This is not always needed, especially for different listeners. Most times, with other listening types unlike touching listeners, you would just place this:
function onTouch() end
But back to what we're looking at. The tag is the object that touched the brick. You can play with this object for fun later. Now notice also two lines below the function: "end". You will need one of these for every function and other aspect of scripting, such as "if" statements. Always remember this when scripting.
Now, make the lines from first example, except put it two lines under the tag, and one line above the listener.
Modifying Objects/Tags
The script knows the brick, will wait until it's touched, and has the function to use. But it doesn't know what to do to the brick.
This is where tagging objects saves you time. We wanted it to flicker invisible/visible, so here's an example:
brick.Transparency = 1 wait(1) brick.Transparency = 0
These lines will alter the brick as we wanted. The brick's transparency is changed to "1", which is completely invisible. The "wait(1)" line will make the script wait for one second before continuing, then the brick's transparency will be put back at 0, which is completely visible. You can alter "wait(1)" to any number inside the parentheses. Whatever number you put inside the parenthesis will be the amount of time it will wait in seconds.
Put those 3 lines right under the line "function onTouch(part)" and above the line "end".
Complete script
brick = game.Workspace.Brick --tagging the brick function onTouch(part) --the function brick.Transparency = 1 --what the function is to do with the brick wait(1) brick.Transparency = 0 end brick.Touched:connect(onTouch) --listening event
Advanced scripting techniques
Now that you can put scripts in your place, now they have to do something useful.
Make your own functions
While scripting, you may want to make your own function to call later. This is easy enough, here is the syntax (grammer) for doing so: (NOTE: These functions are called without a colon [:])
function <functionname>(<args>) <statements> end <functionname>(<arguments>)
An argument is a way to give data to a function. An example of an argument: a Humanoid has a takeDamage() function. You have to tell it how much damage to take. You would type Humanoid:takeDamage(100) to take 100 damage. (NOTE: the takeDamage function will not take damage if the humanoid has a ForceField. Use this function for weapons instead of directly setting the health, to prevent spawnkillers)
Functions can also return a value, which means they can be used instead of a constant (like a number) or a variable (covered below):
function <functionname>(<args>) <statements> return <valueobtainedfromstatements> end <somevariable> = <functionname>(<args>)
Copy and paste these codes into a script for a better example:
Example 1
function sayHello(name)
print("Hello, " .. name .. "!")
end
sayHello("Bob")
Example 2
function addNumbers(a,b) ans = a + b return ans end answer = addNumbers(1,2) print(answer) --> Prints in the output 3
Combining Strings Note the ".." in Example 1. That means to squish two pieces of text (also called strings) together. So "Hello" .. "World" would be "HelloWorld" (note the lack of a space), and "Hello " .. "World" would be "Hello World". Also note that a function must be written before it is called. If you wrote "sayHello("Bob")" before "function sayHello(name)", your script would break.
Functions that return values
Also note the return statement in Example 2. The return statement automatically ends the function at that line, and then gives the value to the variable on the LEFT SIDE of the equals sign. Let's look at that again, this time with detailed comments:
--Define a function called addNumbers with the arguments "a" and "b" function addNumbers(a,b) --make a variable called "ans", and set it to the sum of a and b. ans = a + b --Return the variable called ans. This ends the function. return ans end --Set a variable called "answer" to the return value (ans) of addNumbers, with the arguments 1 and 2. answer = addNumbers(1,2) print(answer) -- Prints in the output 3
Flow control
Flow control basically means doing different things depending on the situation. There are two main ways to do it in Lua, both involve conditions.
Conditions
A condition is a situation. A simple condition is this:
1 == 2
(Note the "==". Always use that, and not "=". If you don't... well, it won't be pretty.) Of course 1 isn't 2! So that would be false.
1 < 2
That would be true, because 1 is less than 2.
If statements
The if statement does something only if a condition is true. Syntax:
if (<condition>) then <statements> end
Example:
if (2 + 2 == 4) then
print("All is right in the world")
end
That would always print "All is right in the world", because 2 + 2 is always equal to 4.
There is also an else statement, which executes if the condition is false:
if (<condition>) then <statements> else <statements> end
Example:
if (2 + 2 == 4) then
print("All is right in the world")
else
print("Warning! Warning! Computer Self-Destruction!")
end
While
while <condition> do <statements> end
This does something over and over until the condition is false, or the break command is executed. People typically don't use this unless they want a never-ending loop, in which case their condition is true, and the loop will not terminate. Here is something very important: If this is an infinite loop, you MUST put a wait() function in your loop! Otherwise your computer/server will take every ounce of it's processing power to execute the code, because right when it's done, it wants to execute again. This WILL crash the server. This will make it wait so it has time to execute other things, and not crash.
Example:
while true do
print("Lagging up your computer...")
wait(0.5)
end
Event Handlers
[TODO: write Event Handler tutorial]
Types and Values
A value is of a specific type. For instance, the value 10 is a number. The value "Bright red" is a text value. Roblox supports these basic Lua types: nil, boolean, number, string, and table. In addition, it supports these more advanced types: function, userdata, thread.
These are examples of the values for each type:
- String: A grouping of characters, such as letters, numbers, and symbols. (examples: "Hello", "Goodbye", the name of a brick)
- Number: Any real number. (examples: 5, -2, 0.5, the value of pi, the transparency of a brick)
- Boolean: A value equaling true or false. (examples: true, false, yes or no, on or off)
- Table: A list of values. A table can contain values of all types (examples: the children of the Workspace)
- Nil: A state of non-existence, nothingness, not zero, but not existing. It usually represents the absence of a useful value.
Variables
Variables are essential to use in a good script. Basically, a variable is a value you can store, then retrieve and/or change it later. Defining a variable is the very easy, as well. To define a variable, just type "variableName = initial value"
greeting = "hello" luckyNumber = 3 brick_5 = "green" variableIDon'tWantToDefineJustYet = nil
To change a variable, you just do do the same thing, only after the variable is defined:
the_variable = 1 -- The definition of "the_variable" print(the_variable) -- Prints "1" in the output. the_variable = 7 -- Making "the_variable" equal 7. print(the_variable) -- Prints "7" in the output. Not 8. we did not add. the_variable = the_variable + 5 -- Making "the_variable" increment by 5. print(the_variable) -- Prints "12" in the output.
Local Variables A local variable is a variable only known ONLY to the script that defines it. To define one you have to say local before it, Here is an example:
local var1 = "Hello" -- Defines var1 as "Hello".
Normal Variables A normal variable is a variable that CHANGES the value it holds. You do not need to put in local. Look at this situation. Let's say "trans" is the Transparency of a brick. The transparency = 0.5
var1 = trans var1 = 0 -- On this line, the transparency would be 0. A local variable would only change var1 to 0. This will change both!
Global Varables You know local and normal variables, but what is a global variable? A global variable is a variable that is "readable" by all scripts. One is "game". When you state "game" it thinks of the Data Model that is you game. To define one, you state "_G."(no space)then the variable name. Then when another script states the variable, it will think of the variable you set it to. Only the script that defines the global variable can change it. Look at this stiuation: Script 1
_G.var1 = 10 -- This line defines a global variable "var1" and it equals 10.
Script2
print(var1) -- Prints 10 in the output!
With all these types of variables, you need to know which is best to use.
"Deleting" a Variable
Let's say you do not want a variable to be used any more. You make the variable's value equal nil.
variable = nil -- The variable "variable" no longer exists.
See also
Scripting
The Class Reference
Edit
Roblox Studio
Script
Workspace
Scripting
Beginner's Guide to Advanced Scripting
In-Depth Scripting Guide
Tutorials