Polar equations: Difference between revisions
>Mindraker No edit summary |
>Mindraker No edit summary |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
Other curves can be set by changing the value of k, as seen in the table. | Other curves can be set by changing the value of k, as seen in the table. | ||
== 3-D images == | |||
Similarly, 3-D images can be created with polar equations. The formula for a sphere in polar is rho = R. Using the formula to convert to Cartesian:<br> | |||
x=r*sin(theta)*cos(phi)<br> | |||
y=r*sin(theta)*sin(phi)<br> | |||
z=r*cos(theta)<br> | |||
The formula rho = R is obvious below.<br> | |||
[[Image:Hollowspherepolar.PNG|thumb|Hollow sphere]] | |||
<pre> | |||
for i = 1,10, 1 do | |||
for j = 1,10, .1 do | |||
R=4 | |||
x=R*math.sin(i)*math.cos(j) | |||
y=R*math.sin(i)*math.sin(j) | |||
z=R*math.cos(i) | |||
p = Instance.new("Part") | |||
p.CFrame = CFrame.new(Vector3.new(10*x, 10*y, 10*z)) | |||
p.Size = Vector3.new(8,8,8) | |||
p.Anchored = true | |||
p.BottomSurface = "Smooth" | |||
p.TopSurface = "Smooth" | |||
p.Parent = game.Workspace | |||
p.BrickColor = BrickColor.new(217) | |||
end | |||
end | |||
</pre> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 21:09, 30 December 2008
Introduction
Roblox operates using the Cartesian coordinate system. This is a gridlike system much like the tiles on the floor of a bathroom. This system is ideal for certain things, e.g., straight lines, roads, buildings, tiles. It is not as good for other things, such as spirals. Another system, called the Polar coordinate system based on an angle and the distance from the center of a map, is much better suited for this.
The problem with this is that you need to convert from the Polar system to the Cartesian system, because Roblox operates in the Cartesian system. This is actually easy enough to do, if you have a formula in the Polar system. Let's take the Quadrifolium from Wikipedia. Its polar equation is:
r=math.cos(2*θ)
So, to obtain the values for x and z, we have to multiply r as follows:
x = r * math.cos(θ)
z = r * math.sin(θ)
We now get:
x=math.cos(2*i) * math.cos(θ)
z=math.cos(2*i) * math.sin(θ)
You will see these formulas again in the script below.

for i = 1,500, 1 do
n=2
d=1
k = n/d
x=math.cos(k*i) * math.cos(i)
z=math.cos(k*i) * math.sin(i)
p = Instance.new("Part")
p.CFrame = CFrame.new(Vector3.new(100*x, 100, 100*z))
p.Size = Vector3.new(8,8,8)
p.Anchored = true
p.BottomSurface = "Smooth"
p.TopSurface = "Smooth"
p.Parent = game.Workspace
p.BrickColor = BrickColor.new(217)
end

for i = 1,500, 1 do
n=3
d=2
k = n/d
x=math.cos(k*i) * math.cos(i)
z=math.cos(k*i) * math.sin(i)
p = Instance.new("Part")
p.CFrame = CFrame.new(Vector3.new(100*x, 100, 100*z))
p.Size = Vector3.new(8,8,8)
p.Anchored = true
p.BottomSurface = "Smooth"
p.TopSurface = "Smooth"
p.Parent = game.Workspace
p.BrickColor = BrickColor.new(217)
end
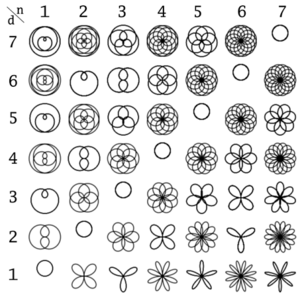
Other curves can be set by changing the value of k, as seen in the table.
3-D images
Similarly, 3-D images can be created with polar equations. The formula for a sphere in polar is rho = R. Using the formula to convert to Cartesian:
x=r*sin(theta)*cos(phi)
y=r*sin(theta)*sin(phi)
z=r*cos(theta)
The formula rho = R is obvious below.

for i = 1,10, 1 do
for j = 1,10, .1 do
R=4
x=R*math.sin(i)*math.cos(j)
y=R*math.sin(i)*math.sin(j)
z=R*math.cos(i)
p = Instance.new("Part")
p.CFrame = CFrame.new(Vector3.new(10*x, 10*y, 10*z))
p.Size = Vector3.new(8,8,8)
p.Anchored = true
p.BottomSurface = "Smooth"
p.TopSurface = "Smooth"
p.Parent = game.Workspace
p.BrickColor = BrickColor.new(217)
end
end