Random terrain: Difference between revisions
>Sduke524 No edit summary |
m Add the CatUp |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Procedurally generated terrain, often refered to as randomly generated terrain, is a terrain that is created via script rather than by hand. This gives the ability to have a game that is a completely different experience every time | {{CatUp|Tutorials}} | ||
Procedurally generated terrain, often refered to as randomly generated terrain, is a terrain that is created via script rather than by hand. This gives the ability to have a game that is a completely different experience every time while using a lot less work. | |||
== The basic algorithm == | == The basic algorithm == | ||
The most basic algorithm is to place bricks of random size in random positions across your baseplate. To do this we will set up a simple for loop that instances a new, anchored part every time. | The most basic algorithm is to place bricks of random size in random positions across your baseplate. To do this we will set up a simple for loop that instances a new, anchored part every time. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
for i = 1, 200 do | |||
local part = Instance.new("Part", workspace) -- Creates a Part and makes it a descendant of Workspace | |||
part.Anchored = true -- Prevents the part from moving. | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Next we will set the size to a random amount. For this we will use the function ''math.random()'' | Next we will set the size to a random amount. For this we will use the function ''math.random()'' | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
part.Size = Vector3.new(math.random(1, 20), math.random(1, 20), math.random(1, 20)) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
This will set the Size to a random amount between 1 and 20 for the X,Y and Z size. Now for the last step of our algorithm, use CFrame to place the brick in a random spot. We will easily just place the X and Z axis using ''math.random()'' yet for the Y axis, we'll have to do something special. Being that we want all the bricks to stay on the ground, we want their base to be at 0. Now since the Position of a brick in roblox uses the center of the brick, we'll have to divide the Y size in half, so that it sits just perfectly on 0. So it would be : | This will set the Size to a random amount between 1 and 20 for the X,Y and Z size. Now for the last step of our algorithm, use CFrame to place the brick in a random spot. We will easily just place the X and Z axis using ''math.random()'' yet for the Y axis, we'll have to do something special. Being that we want all the bricks to stay on the ground, we want their base to be at 0. Now since the Position of a brick in roblox uses the center of the brick, we'll have to divide the Y size in half, so that it sits just perfectly on 0. So it would be : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(math.random(-100, 100), part.Size.Y/2, math.random(-100, 100)) | |||
end -- for the for loop | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
[[Image:Basic_terrain.PNG|center|200px|The basic algorithm]] | |||
== Heightmap == | == Heightmap == | ||
A heightmap shows different elevations across the whole map. For making a basic one, we will just have a script in the base of our map. This way we can specify the size of the map we want and where it will be positioned, easily. To start, we will define three variables. | A heightmap shows different elevations across the whole map. For making a basic one, we will just have a script in the base of our map. This way we can specify the size of the map we want and where it will be positioned, easily. To start, we will define three variables. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
local size = Vector3.new(10, -- Number of tiles along the width | |||
10, -- Number of steps of heightmap | |||
10) -- Number of tiles along the length | |||
local base = script.Parent -- The part to replace with terrain | |||
local tilePart = Instance.new("Part") | |||
tilePart.Anchored = true | |||
tilePart.formFactor = "Custom" | |||
tilePart.Size = base.Size / size --The size of one unit or cuboid of the map | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Now, how we will create all the bricks is similar to how we did it last time, only now it will use two "for" loops. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
for x = 1, size.x do | |||
for z = 1, size.z do | |||
local y = math.random(size.y) | |||
local tile = tilePart:clone() | |||
local position = Vector3.new(x-1, 0, z-1) * tile.Size | |||
tile.Size = tile.Size * Vector3.new(1, y, 1) | |||
tile.CFrame = CFrame.new(tile.Size/2) --Shift the part by half it's size, so we can position the corner | |||
tile.CFrame = tile.CFrame - base.Size / 2 --Shift it into one corner of the base | |||
tile.CFrame = tile.CFrame + position --Put it in the right place | |||
tile.CFrame = base.CFrame * tile.CFrame --Move it so that it is level with the surface of the base | |||
tile.Parent = workspace | |||
end | |||
end -- an end for each for loop | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
[[Image:TerrainH.PNG|center|200px]] | |||
== Coloring the bricks == | == Coloring the bricks == | ||
Sadly, in case you haven't noticed, the bricks are all completely dull and grey. So to change this we will make a simple function named "color". | |||
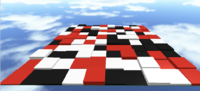
=== Randomly Picked === | |||
=== | For this method, we'll use a table full of colors. Then the function will pick a random color out of the table and use it. Here is the function | ||
For this method, we'll use a table full of | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
local colors = {BrickColor.Red(), BrickColor.Black(), BrickColor.White()} | |||
function color(part) | |||
part.BrickColor = colors[math.random(#colors)] | |||
Now all you have to do to use this function is somewhere in the script put | end | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Now all you have to do to use this function is somewhere in the script put ''color(a)'' | |||
and it will run. | and it will run. | ||
[[Image:Colorful.PNG|center|200px]] | |||
=== Based on height === | === Based on height === | ||
Now we will base are function off of the height of the brick. It will be basically the same thing, with one real difference. Now we will have | Now we will base are function off of the height of the brick. It will be basically the same thing, with one real difference. Now we will have a couple of conditionals and the "color(a)" will have to go after the brick is sized. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
local colors = {BrickColor.Red(), BrickColor.Black(), BrickColor.White()} | |||
function color(part) | |||
if part.Size.Y > 7 then | |||
part.BrickColor = colors[3] | |||
elseif part.Size.Y > 3 then | |||
part.BrickColor = colors[2] | |||
else | |||
part.BrickColor = colors[1] | |||
end | |||
end | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Using weighted values == | == Using weighted values == | ||
In scripting terminology, weighted means numbers adjusted to seem more proportional towards what you want. | In scripting terminology, weighted means numbers adjusted to seem more proportional towards what you want. | ||
=== Mountains === | === Mountains === | ||
In case we wanted to make sure a mountain came out of our script, we can easily just use a variable ( rand ) to hold the highest point we reach and add that to every number. Now to maintain it being random, we will also add a random number between -2 and 2. Then after we have that number, we'll check if the random number between -2 and 2 is greater than 0 and add it to our variable rand. | In case we wanted to make sure a mountain came out of our script, we can easily just use a variable ( rand ) to hold the highest point we reach and add that to every number. Now to maintain it being random, we will also add a random number between -2 and 2. Then after we have that number, we'll check if the random number between -2 and 2 is greater than 0 and add it to our variable "rand". | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
rand=0 | |||
for x=1,Xlength do | |||
for z=1,Zlength do | |||
local a=part:clone() | |||
local random_factor=math.random(-2,2) | |||
tilePart.Size=Vector3.new(part.Size.X/Xlength,rand+random_factor,par.Size.Z/Zlength) | |||
if random_factor>0 then | |||
rand=rand+random_factor | |||
end | end | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
[[Image:Mountain.PNG|center|200px]] | |||
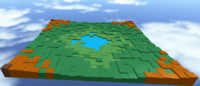
=== Lake === | === Lake === | ||
Now to make a lake, we won't need random_factor or rand. All that will be needed is a little bit of math to add in the weighted factors. Just try | Now to make a lake, we won't need random_factor or rand. All that will be needed is a little bit of math to add in the weighted factors. Just try | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | |||
tilePart.Size=Vector3.new(par.Size.X/Xlength,math.random(-2,2)+math.abs(x-Xlength/2)+math.abs(z-Zlength),par.Size.Z/Zlength) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Now this works because it will subtract half of the number of bricks from x, putting x in the middle, then taking the absolute value of that and adding it with the same thing for z. | |||
[[Image:Random_lake.PNG|center|200px]] | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Terrain Generation|Generating non-random, mathematical terrain]] | |||
[[Category:Scripting Tutorials]] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 26 April 2023
Procedurally generated terrain, often refered to as randomly generated terrain, is a terrain that is created via script rather than by hand. This gives the ability to have a game that is a completely different experience every time while using a lot less work.
The basic algorithm
The most basic algorithm is to place bricks of random size in random positions across your baseplate. To do this we will set up a simple for loop that instances a new, anchored part every time.
for i = 1, 200 do
local part = Instance.new("Part", workspace) -- Creates a Part and makes it a descendant of Workspace
part.Anchored = true -- Prevents the part from moving.
Next we will set the size to a random amount. For this we will use the function math.random()
part.Size = Vector3.new(math.random(1, 20), math.random(1, 20), math.random(1, 20))
This will set the Size to a random amount between 1 and 20 for the X,Y and Z size. Now for the last step of our algorithm, use CFrame to place the brick in a random spot. We will easily just place the X and Z axis using math.random() yet for the Y axis, we'll have to do something special. Being that we want all the bricks to stay on the ground, we want their base to be at 0. Now since the Position of a brick in roblox uses the center of the brick, we'll have to divide the Y size in half, so that it sits just perfectly on 0. So it would be :
part.CFrame = CFrame.new(math.random(-100, 100), part.Size.Y/2, math.random(-100, 100))
end -- for the for loop
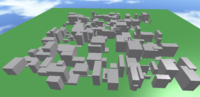
Heightmap
A heightmap shows different elevations across the whole map. For making a basic one, we will just have a script in the base of our map. This way we can specify the size of the map we want and where it will be positioned, easily. To start, we will define three variables.
local size = Vector3.new(10, -- Number of tiles along the width
10, -- Number of steps of heightmap
10) -- Number of tiles along the length
local base = script.Parent -- The part to replace with terrain
local tilePart = Instance.new("Part")
tilePart.Anchored = true
tilePart.formFactor = "Custom"
tilePart.Size = base.Size / size --The size of one unit or cuboid of the map
Now, how we will create all the bricks is similar to how we did it last time, only now it will use two "for" loops.
for x = 1, size.x do
for z = 1, size.z do
local y = math.random(size.y)
local tile = tilePart:clone()
local position = Vector3.new(x-1, 0, z-1) * tile.Size
tile.Size = tile.Size * Vector3.new(1, y, 1)
tile.CFrame = CFrame.new(tile.Size/2) --Shift the part by half it's size, so we can position the corner
tile.CFrame = tile.CFrame - base.Size / 2 --Shift it into one corner of the base
tile.CFrame = tile.CFrame + position --Put it in the right place
tile.CFrame = base.CFrame * tile.CFrame --Move it so that it is level with the surface of the base
tile.Parent = workspace
end
end -- an end for each for loop

Coloring the bricks
Sadly, in case you haven't noticed, the bricks are all completely dull and grey. So to change this we will make a simple function named "color".
Randomly Picked
For this method, we'll use a table full of colors. Then the function will pick a random color out of the table and use it. Here is the function
local colors = {BrickColor.Red(), BrickColor.Black(), BrickColor.White()}
function color(part)
part.BrickColor = colors[math.random(#colors)]
end
Now all you have to do to use this function is somewhere in the script put color(a) and it will run.
Based on height
Now we will base are function off of the height of the brick. It will be basically the same thing, with one real difference. Now we will have a couple of conditionals and the "color(a)" will have to go after the brick is sized.
local colors = {BrickColor.Red(), BrickColor.Black(), BrickColor.White()}
function color(part)
if part.Size.Y > 7 then
part.BrickColor = colors[3]
elseif part.Size.Y > 3 then
part.BrickColor = colors[2]
else
part.BrickColor = colors[1]
end
end
Using weighted values
In scripting terminology, weighted means numbers adjusted to seem more proportional towards what you want.
Mountains
In case we wanted to make sure a mountain came out of our script, we can easily just use a variable ( rand ) to hold the highest point we reach and add that to every number. Now to maintain it being random, we will also add a random number between -2 and 2. Then after we have that number, we'll check if the random number between -2 and 2 is greater than 0 and add it to our variable "rand".
rand=0
for x=1,Xlength do
for z=1,Zlength do
local a=part:clone()
local random_factor=math.random(-2,2)
tilePart.Size=Vector3.new(part.Size.X/Xlength,rand+random_factor,par.Size.Z/Zlength)
if random_factor>0 then
rand=rand+random_factor
end

Lake
Now to make a lake, we won't need random_factor or rand. All that will be needed is a little bit of math to add in the weighted factors. Just try
tilePart.Size=Vector3.new(par.Size.X/Xlength,math.random(-2,2)+math.abs(x-Xlength/2)+math.abs(z-Zlength),par.Size.Z/Zlength)
Now this works because it will subtract half of the number of bricks from x, putting x in the middle, then taking the absolute value of that and adding it with the same thing for z.